Adult Strabismus – Back To Basics:
Is treatment available for adult strabismus?
Yes, treatment options are available for adult strabismus, and these treatments have a high success rate. Adult strabismus is a complex field of ophthalmology, where the cause of the strabismus and the type of strabismus dictate the treatments that will be successful. Often surgery is recommended, and sometimes eye exercises, glasses or prisms are used too.
Signs and symptoms of adult strabismus:
Adult strabismus is not just a cosmetic concern. People with strabismus often avoid making eye contact, are self-conscious about how they look, and are worried people get distracted by their eye wandering. This can lead to challenges in communication and the potential for avoidance and psychosocial issues. Adult strabismus can also cause debilitating double vision, and asthenopic symptoms such as headache and eye strain.
Treatment for adult strabismus:
Treatment options are largely dependant on the type of strabismus. Your ophthalmologist is the most qualified person to talk you through the treatment options available that will be most successful for your individual strabismus. Here we have outlined a few methods often used for treating strabismus in adults:
– Glasses: Strabismus can sometimes be partially or completely controlled by wearing correctly prescribed glasses. Conversely, certain glasses will have the opposite effect on some forms of strabismus, and may make eye strain or double vision worse. If you have strabismus, make sure you have glasses prescribed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist with experience in treating strabismus.
– Eye exercises (orthoptics): Eye exercises are successful in treating some forms of adult strabismus if they are taught correctly and performed accurately with good compliance from the patient. Eye exercises for adult strabismus are usually only used in the case of intermittent exotropia.
– Prisms: Prisms can be used to align the eyes, alleviate eye strain, and help eliminate double vision in certain types of adult strabismus. Prisms can be used in stick-on form on glasses, or can be ground into glasses.
– Botox: Botulinum toxin can be used to treat certain types of adult strabismus. The Botox is injected into a strong or overacting extra ocular muscle, to relax the muscle force and align the eyes.
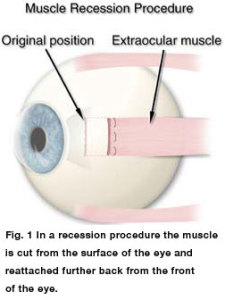
– Surgery: Strabismus surgery is the most commonly prescribed treatment for adult strabismus, and in most cases it is the best way of treating adult strabismus successfully.
Strabismus surgery for adult strabismus:
Strabismus surgery aims to align the eyes by loosening or tightening one or more of the extraocular muscles of the eye.
In recent years, there has been a push for education about adult strabismus surgery being more than purely a cosmetic procedure. In support of this, studies have recently been published which demonstrate the psychosocial benefits of adult strabismus surgery, including a study published in 2014 by Sydney Ophthalmic Specialists ophthalmologist Dr Frank Martin and orthoptist Sarita Beukes: http://www.e-tjo.com/article/S2211-5056(13)00079-3/abstract?cc=y=
Strabismus surgery in adults is usually performed as day surgery under local anaesthesia with sedation. If you prefer, arrangements can be made to have strabismus surgery under general anaesthesia.
Many people mistakenly believe that the eyeball is removed from the eye socket during eye surgery. This is certainly not the case for strabismus surgery. The muscle or muscles to be operated on are accessed by gently positioning the eye to different positions to gain access to the muscles. No incisions are made on the skin.
Surgical treatment of strabismus is based on the size of the strabismus. your ophthalmologist will take detailed measurements of the size of your strabismus before surgery.
What is amblyopia:
Amblyopia is a condition where vision fails to develop normally in childhood. Amblyopia develops because of a problem with the brain and the eye working together, and persists regardless of wearing glasses or contact lenses. Amblyopia is usually present in one eye only, but can occur in both eyes. An amblyopic eye often looks normal, and can be caused by any condition that prevents the eye from focussing clearly.
The gold standard treatment for amblyopia is occlusion therapy, commonly known as patching. This is where a patch is worn over the stronger eye to help the brain to eye connections form in the weaker, amblyopic eye. Patching is usually prescribed in childhood, and recent studies have shown some success in patching of older, adolescent individuals. Patching has been shown to have minimal success in adult amblyopia.
Recent studies have investigated new treatments for adult amblyopia, with some showing surprisingly good results. The most successful of these to date has been dichoptic therapy. Sydney ophthalmic specialists is currently running a trial of dichoptic therapy for children over the age of 6 years, and adults. If you would like more information about our dichoptic therapy trial for amblyopia, please email clinical@sosdoctors.com.au or phone (02) 9241 2913.
References:
https://aapos.org/terms/conditions/11
https://aapos.org/terms/conditions/100
https://aapos.org/terms/conditions/102
https://ranzco.edu/ArticleDocuments/233/opa_ranzco_strabismus_surgery.pdf.aspx?Embed=Y